Who’s a gardener’s BFF?
A beneficial nematode, of course.
Nematodes are tiny, worm-like organisms that live in soil and water. There are 25,000 species, some of which are harmful and others highly beneficial.
In your garden, they can control grubs, root borers, cutworms, and other plant pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Types of Nematodes
Beneficial Nematodes
- These are pest control heroes in the gardening world.
- They attack and destroy harmful pests, effectively protecting your plants.
- Commonly used species include Steinernema and Heterorhabditis.
An AI illustration of beneficial nematodes.
Parasitic Nematodes
- Parasitic nematodes are the bad boys who fell in with the wrong crowd.
- Some, like root-knot nematodes, can harm plants by feeding on roots.
The key is to target pests with beneficial nematodes while keeping the bad boys at bay.
How Beneficial Nematodes Control Pests
- Beneficial nematodes actively seek out pests in the soil by sensing carbon dioxide and other chemical signals. They’re especially effective against soil-dwelling pests like grubs, weevils, and cutworms.
- Once they locate a pest, nematodes enter the host’s body through natural openings such as mouthparts or spiracles (breathing holes).
- Inside the host, beneficial nematodes release symbiotic bacteria. These bacteria multiply rapidly, killing the pest within 24 to 48 hours via infection and septicemia.
- The nematodes reproduce inside the dead pest’s body. Multiple generations continue the pest control process. Once they’ve depleted the host’s resources, the new nematodes search for other pests.
- The nematodes are particular to certain pests and don’t harm plants, earthworms, or beneficial insects in the ecosystem.
Where to Buy Beneficial Nematodes
You can purchase beneficial nematodes from a local garden center like Anawalt or an online retailer. They’re typically sold in small refrigerated packages that hold the nematodes in an inert carrier material like clay or gel.
These packages keep the nematodes dormant and viable until you apply them. Always check the expiration date and follow storage instructions to ensure their effectiveness.

Beneficial nematodes won’t harm earthworms, ladybugs, birds, and other beneficial organisms.
When & Where to Use Beneficial Nematodes
- Apply nematodes in the early morning or late evening to avoid direct sunlight, which can kill them.
- Plan treatments for spring or fall when soil temperature falls between 55°F to 85°F.
- Nematodes thrive both in soil beds and potting soil. Whether dealing with pests in a vegetable patch or your indoor herb garden, they can help.
- Focus nematode applications on areas where pests are most active, such as root zones or shaded, damp areas.
How to Apply Beneficial Nematodes
1. Select the Right Nematodes
Different nematode species target different pests:
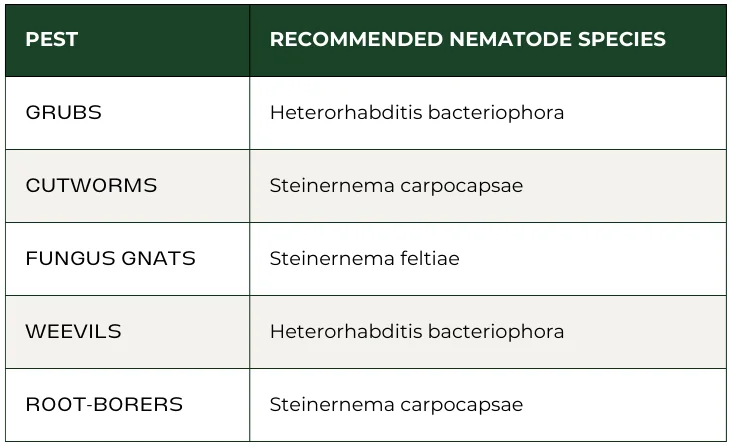
- For grubs and weevils, choose Heterorhabditis bacteriophora.
- For fungus gnats and cutworms, go for Steinernema feltiae.
2. Prepare the Nematodes
- Purchase your nematodes in a concentrated form from a garden supply store or online.
- Follow the package instructions to mix the nematode solution with water.
3. Water Your Soil
- Moisten the soil before application. Moisture helps nematodes move through the soil to find their prey.
4. Apply the Nematodes
- Use a sprayer or watering can to evenly distribute the nematode solution across your target areas.
- Focus on areas affected by pests.

These handsome microorganisms are your ticket to organic pest control and garden health.
5. Maintain Soil Moisture
- Keep the soil damp for at least two weeks after application to help nematodes establish themselves.
6. Monitor Results
- Over time, observe changes in pest populations. Repeat applications may be needed depending on the severity of the infestation.
Tips for Success
- Avoid using chemical pesticides, which can kill beneficial nematodes.
- Store unused nematodes in the refrigerator, but apply them before the expiration date for best results.
- Don’t overapply – nematodes are effective even in small numbers.
Common Pests Controlled by Nematodes
Here’s a quick breakdown of pests that beneficial nematodes can manage and the species to use against them.
FAQs: Using Beneficial Nematodes
Q: How long do beneficial nematodes last in the soil?
Depending on environmental conditions, they can stay active and reproduce for up to six months. You may need regular applications for long-lasting pest control.
Q: Will nematodes harm my plants or other beneficial insects?
They only target specific pests and are safe for plants and other non-target organisms.
Q: Can I use beneficial nematodes indoors?
Yes, as long as the soil temperature is within the recommended range and moisture levels are maintained.
Q: How do I know if the nematodes are working?
You may notice reduced pest activity within one to two weeks. Dead pests may also be visible in the soil as nematodes eliminate their hosts.
Q: Can beneficial nematodes survive winter?
Nematodes typically go dormant when soil temperatures drop below 55°F. However, extreme freezing conditions can kill them, so reapplication might be necessary in the spring.
Q: Are nematodes safe for pets and humans?
When used as directed, beneficial nematodes pose no risk to humans, pets, or wildlife. They target only specific soil-dwelling pests.
Q: How often should I reapply nematodes?
Application timing can vary depending on seasonal pest activity and environmental conditions, but it should be every 4 to 6 months or as needed.
Q: Can nematodes be used in conjunction with other biological controls?
Nematodes can be safely used with other biological pest control measures, such as predatory insects or organic sprays, for comprehensive pest management.